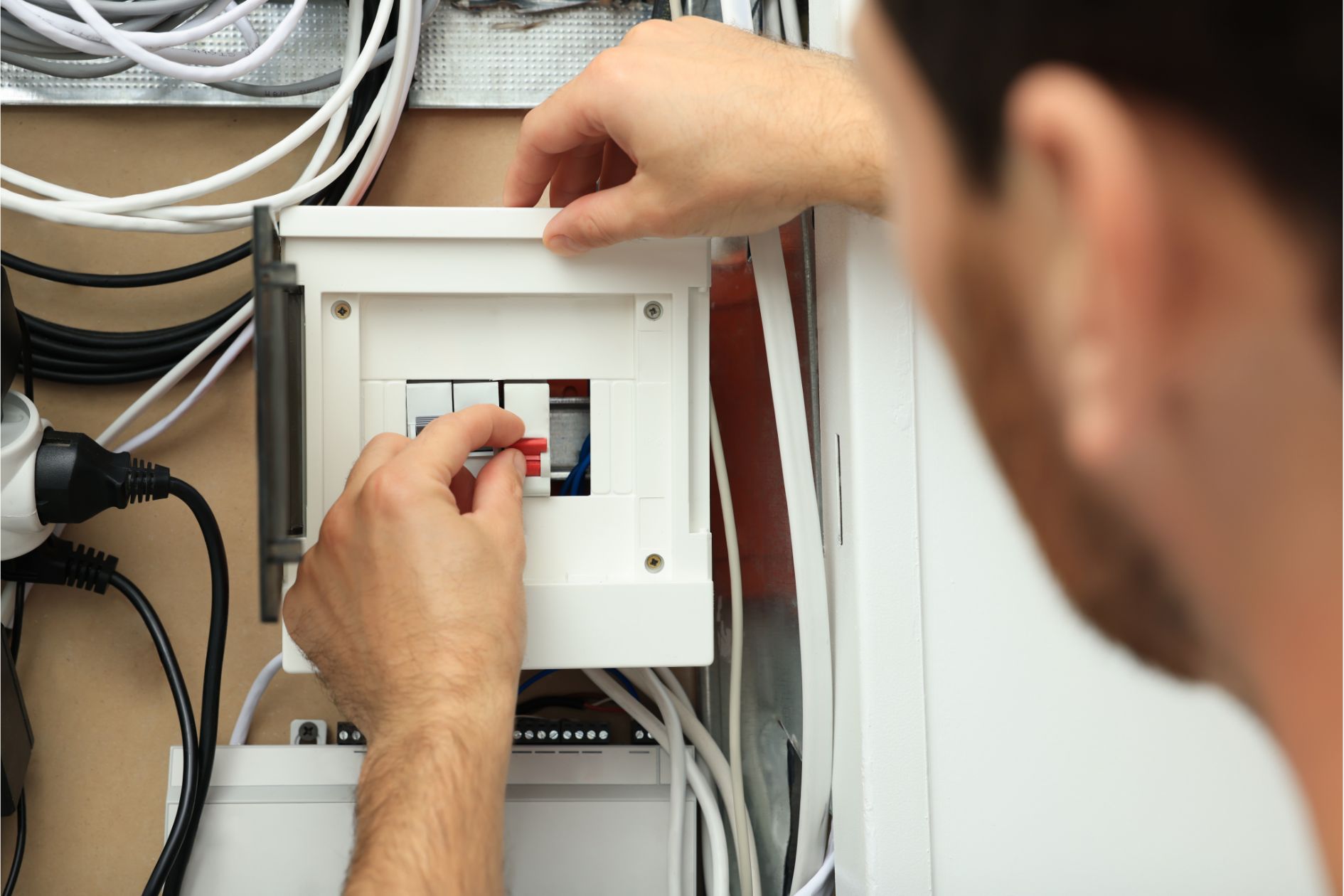
Troubleshooting Electrical Supplies: When to Replace and Upgrade
In today’s modern world, electricity is an essential part of our daily lives. From powering our homes to fueling our devices, electrical supplies play a crucial role in keeping everything running smoothly. However, like any other system, electrical supplies may encounter problems over time. This article will guide you through the process of troubleshooting electrical supplies, determining when to replace them, and exploring the benefits of upgrading to newer models.
Understanding Electrical Supplies
No matter where you are, electrical supplies are everywhere. They encompass a wide range of components, including wires, switches, outlets, and circuit breaker. Understanding the basics of electrical supplies is essential for effective troubleshooting and maintenance.
The Basics of Electrical Supplies
To comprehend electrical supplies, one must start with the fundamentals. Electricity flows through conductive materials, such as copper wires. Circuit breakers act as safety devices, preventing overloads or short circuits. Switches control the flow of electricity through a circuit, while outlets provide access to electrical power.
Let’s delve deeper into the world of electrical supplies. Copper wires, for example, are the most commonly used conductive material due to their excellent electrical conductivity and affordability. These wires come in different gauges, each suitable for specific applications. Thicker wires are used for high-power circuits, while thinner wires are ideal for low-power applications.
Now, let’s talk about circuit breakers. These crucial components protect electrical circuits from damage caused by excessive current flow. When the current exceeds a safe level, the circuit breaker trips, interrupting the flow of electricity. This prevents overheating and potential fires. Circuit breakers are available in various sizes and types, such as thermal-magnetic and ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs).
Switches, on the other hand, play a vital role in controlling the flow of electricity within a circuit. They allow users to turn lights on or off, activate appliances, and control the operation of various electrical devices. Switches come in different forms, including toggle switches, rocker switches, and dimmer switches, each serving a specific purpose and aesthetic preference.
Lastly, outlets provide the means to access electrical power. There are different types of outlets, each designed for specific applications and safety requirements. Standard outlets, also known as duplex outlets, are the most common type found in homes and commercial buildings. They provide two receptacles for plugging in electrical devices. If you want to read about Key Aspects a Brisbane Buyers Agent Can Assist With you can visit https://charlesfox.net/key-aspects-a-brisbane-buyers-agent-can-assist-with/
GFCI outlets, on the other hand, have built-in ground fault circuit interrupters that protect against electrical shock. These outlets are commonly installed in areas where water is present, such as kitchens and bathrooms. Additionally, AFCI outlets are equipped with arc fault circuit interrupters, which detect and prevent electrical arcs that can cause fires.
Common Types of Electrical Supplies
Electrical supplies come in various types, each serving a specific purpose. Fuses and circuit breakers protect against power surges and regulate the flow of electricity. Outlets can have different designs, such as standard, GFCI, or AFCI outlets, catering to specific requirements. Understanding these types is crucial for troubleshooting issues related to them.
Let’s explore the different types of electrical supplies in more detail. Fuses are devices that protect electrical circuits by melting and breaking the circuit when there is an excessive flow of current. They are typically made of a metal wire or strip that melts at a specific current rating, thus interrupting the circuit. Fuses need to be replaced once they blow, while circuit breakers can be reset after tripping.
As mentioned earlier, circuit breakers are essential for protecting electrical circuits from overloads and short circuits. They are available in different sizes and types to accommodate various electrical systems and applications. Thermal-magnetic circuit breakers combine thermal and magnetic trip mechanisms to provide reliable protection against both high and low-level faults. Ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs) are specifically designed to protect against electrical shock caused by ground faults, which occur when current flows through an unintended path, such as a person or water. Arc fault circuit interrupters (AFCIs), as discussed earlier, detect and prevent electrical arcs that can cause fires.
In addition to fuses and circuit breakers, there are various types of outlets that serve different purposes. Standard outlets, also known as duplex outlets, are the most common type found in residential and commercial buildings. They provide two receptacles for plugging in electrical devices. GFCI outlets, as mentioned earlier, have built-in ground fault circuit interrupters that provide an extra layer of protection against electrical shock. These outlets are commonly installed in areas where water is present, such as kitchens, bathrooms, and outdoor spaces. AFCI outlets, on the other hand, are equipped with arc fault circuit interrupters and are designed to prevent electrical arcs that can cause fires.
By understanding the different types of electrical supplies and their functions, you can effectively troubleshoot electrical issues and ensure the safety and efficiency of your electrical systems.
Troubleshooting Electrical Supplies
Electrical problems can arise due to faulty wiring, damaged components, or incorrect installations. Identifying and addressing these issues is crucial for maintaining a safe and efficient electrical system within your home or office.
When it comes to troubleshooting electrical supplies, there are various factors to consider. Understanding the common problems that can occur is essential in order to effectively diagnose and resolve issues.
Identifying Common Electrical Problems
One of the first steps in troubleshooting electrical supplies is identifying common problems. These may include flickering lights, tripping circuit breakers, or outlets that do not work. Flickering lights can be caused by loose connections, faulty bulbs, or voltage fluctuations. Tripping circuit breakers often indicate an overloaded circuit or a short circuit. Outlets that do not work may be due to loose wiring, a faulty outlet, or a tripped GFCI (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter).
By narrowing down the issue, you can focus troubleshooting efforts on the specific area requiring attention. For example, if you have multiple outlets that are not working, it may indicate a problem with the circuit breaker or a tripped GFCI. On the other hand, if only one outlet is not working, it could be a faulty outlet or loose wiring.
It is important to note that electrical problems can be complex and may require the expertise of a licensed electrician. They have the knowledge and experience to safely diagnose and resolve electrical issues.
Safety Measures During Troubleshooting
While troubleshooting electrical supplies, safety should always be a top priority. Before starting any work, ensure that the power is turned off to prevent electrocution. This can be done by switching off the circuit breaker or removing the fuse associated with the area you will be working on.
Additionally, using insulated gloves and tools can help minimize the risk of accidents. Insulated gloves provide a barrier between your hands and the electrical current, reducing the chance of electric shock. Insulated tools, such as screwdrivers and pliers, have handles made of non-conductive materials to prevent electrical conductivity.
If the task seems complex or you are unsure about how to proceed, it’s best to seek professional assistance to avoid potential hazards. A licensed electrician can safely troubleshoot and resolve electrical problems, ensuring the safety of you and your property.
Remember, electrical troubleshooting requires knowledge, skill, and caution. By following proper safety measures and seeking professional help when needed, you can effectively address electrical issues and maintain a safe electrical system.
When to Replace Electrical Supplies
Electrical supplies, like any other mechanical components, have a limited lifespan. Over time, wear and tear can lead to reduced performance or even complete failure. It is important to recognize the signs indicating when it’s time to replace your electrical supplies.
When it comes to electrical supplies, safety should always be a top priority. Faulty or outdated electrical supplies can pose serious risks such as electrical fires or electrocution. By being proactive and replacing your electrical supplies when necessary, you can ensure the safety and efficiency of your electrical system.
Signs Your Electrical Supplies Need Replacement
If you notice issues such as frequent power surges, dimming lights, or outlets that feel hot to the touch, it’s a clear indication that your electrical supplies need replacement. These signs should never be ignored, as they can be early warning signs of a more significant underlying problem.
Frequent power surges can be caused by various factors, including faulty wiring or overloaded circuits. Dimming lights may indicate loose connections or insufficient power supply. Outlets that feel hot to the touch can be a sign of excessive electrical resistance, which can lead to overheating and potential fire hazards. If you want to read about Power Supply Troubleshooting you can click here.
It is important to address these issues promptly by consulting a qualified electrician who can assess the condition of your electrical supplies and recommend the necessary replacements. Ignoring these signs can lead to further complications, compromising the safety and efficiency of your electrical system.
The Lifespan of Different Electrical Supplies
The lifespan of electrical supplies varies depending on the type and usage. Understanding the lifespan of different electrical supplies can help you plan for their replacement more effectively.
Circuit breakers, for example, typically last around 30 to 40 years. These crucial components protect your electrical system from overloads and short circuits by automatically shutting off the power. However, as they age, circuit breakers may become less reliable and more prone to tripping or failing to trip when needed. Regular inspection and replacement of old circuit breakers can help prevent electrical hazards.
Light switches, on the other hand, may last up to 15 years. Over time, the mechanical components inside the switch can wear out, leading to flickering lights or difficulty in turning them on or off. Upgrading to newer, more durable light switches can improve functionality and enhance the aesthetics of your space.
Other electrical supplies, such as electrical outlets, wiring, and electrical panels, also have their own lifespans. Regular maintenance and periodic inspections by a qualified electrician can help identify any signs of wear and tear and determine when replacement is necessary.
In conclusion, recognizing the signs indicating when to replace your electrical supplies is crucial for maintaining a safe and efficient electrical system. By addressing issues promptly and understanding the lifespan of different electrical supplies, you can ensure the longevity and reliability of your electrical system.
Upgrading Your Electrical Supplies
While replacing faulty electrical supplies is essential, it’s also an opportunity to upgrade your system. Upgrading can enhance safety, improve efficiency, and provide additional functionalities tailored to your specific needs.
Benefits of Upgrading Electrical Supplies
Upgrading your electrical supplies not only ensures a higher level of safety but also offers a range of benefits. Newer components are often more energy-efficient, reducing your electricity bills. Additionally, upgrades may include features like surge protection, USB outlets, or smart home integration.
Choosing the Right Upgrades for Your Needs
When considering upgrades, it’s important to assess your requirements carefully. Determine whether you need additional outlets, enhanced lighting controls, or increased capacity for new appliances. Consulting with an electrician can help you choose the right upgrades that align with your needs and future plans.
The Process of Replacing and Upgrading
Replacing and upgrading electrical supplies can be a complex task. However, with the right approach and proper guidance, it can be accomplished effectively and safely.
Steps to Replace Electrical Supplies
Begin by identifying the specific electrical supplies that require replacement. Turn off the power to the affected area and carefully remove the old components. Install the new supplies following manufacturer guidelines, ensuring proper connections and secure mounting. Finally, test the functionality of the newly installed supplies to guarantee everything is working as expected.
How to Upgrade Your Electrical Supplies Safely
When upgrading your electrical supplies, it’s crucial to adopt a systematic approach. Start by creating a plan outlining the upgrades you want to implement. This may include rewiring, installing new outlets, or upgrading the circuit panel. Prioritize safety by turning off the power and following professional advice when needed.
By understanding electrical supplies, troubleshooting common issues, recognizing when components need replacement, and exploring the benefits of upgrades, you can maintain a safe and efficient electrical system in your home or workplace. Don’t underestimate the importance of regular maintenance and seeking professional assistance when faced with complex problems. By staying proactive, you can ensure the smooth functioning of your electrical supplies for years to come.

